Unlike previous technologies, the spectrum for' > 5G networks is divided into three radically different frequency ranges.
This division is an essential element of this attractive modern technology.
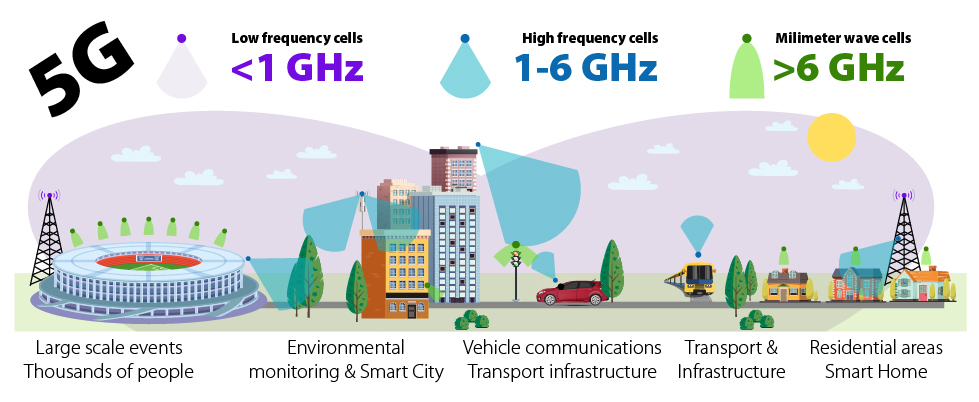
The lower part of the frequency spectrum, which represents a range of frequencies up to 1 GHz, provides excellent signal coverage and penetration, but on the other hand, the transfer rate is limited to 100 Mbps.
The middle part of the 1-6 GHz frequency spectrum represents a compromise between the bit rate (up to 1 Gbps) and the capable range, which decreases proportionally with increasing frequency.
The last largest part of the frequency spectrum includes an area higher than 6 GHz (referred to as mmWave”), with very high bit rates up to 10 Gbps (10,000 Mbit / s) with extremely low latency (connection response). On the other hand, the range of the signal and its penetration are very limited.
Splitting ' >5G technology into three totally different frequency areas allows providing of next-generation networks with high quality coverage, but also with high speed and low delay and maximizing Quality of Service (QoS) as needed.
5G antennas enable faster, more reliable and more efficient communication, which brings improvements not only in download speeds, but also in coverage and reliability for new technological applications. 5G antennas represent a significant technological advance with an impact on a wide range of industries and everyday life.